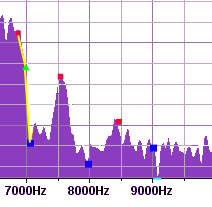
Na prvním obrázku je dobře vidět problém. Mám dva body, červený (výše) a modrý (níže) a chci mezi nimi detekovat bod. Nevím jestli ten bod existuje, ale zajímají mě především tyto věci:
1) Počet "výkyvů" (nebo prostě "frekvence" výkyvů)
2) Jak velké jsou výkyvy? Je to vlastně vyjádřené úhlem, který je na zeleném vrcholu. Vidím, že zde je přibližně úhel 170°.
3) Má žlutá křivka tendenci stoupat nebo klesat (úhel)? Tzn. převyšuje ten červený bod vlevo nebo klesá? A jak moc klesá?
4) Na obrázku níže ale vidím, že situace může být složitější. Dva zelené body jsou vedle sebe a vlastně mají mezi sebou nakloněnou rovinu, takže mě navíc zajímá jestli tato nakloněná rovina existuje a jak moc je nakloněná (úhel). Je zde otázka jestli by se neměl vytvořit ještě jeden světle modrý bod mezi těma zelenýma. Ale tou rovinou by se dalo vyjádřit právě to, že ty body mezi nimi prostě jsou v podobné výši (to je pak vidět u předposlednho obrázku).
U posledního obrázku je více bodů v jedné rovině a tak si říkám že by bylo lepší zde monitorovat existenci takovéto "roviny" - zelené i světle modré body podávají informaci jak moc ta křivka kmitá Jsou to vlastně dvě "mírně hrbolaté" roviny. Pro mě by bylo jednodušší pracovat s touto informací o rovině a její "hrbolatostí" než se sadou informací o mnoha "kmitajících" bodech. Stačí vědět, že od 9000 Hz do 11009Hz je rovina, která má určitý úhel a je lehce rozkmitaná...
Všechny zelené a modré body
sobota 16. listopadu 2019
Fáze 1. nalezení významných bodů křivky
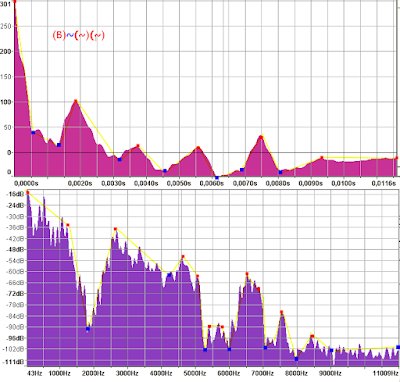
Autokorelace a frekvenční analýza 2 (zmenšené náhledy)
Příklady se slabikou Ba a B~
Vysvětlivky
~ reprezentuje zvuk následující zvuk B
B(a) znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na části písmene B, kde samohláska a nezasahuje do výběru.
(B)a znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na samohlásce "a".
(B)a(a) znamená, že analyzuju část, kde se prolíná "B" s "a", ale ne celý vzorek.
(B)~(~) podobbně analyzuju prostřední část (zvuk ~), kde se míchá B a ~.
(B)~(~)(~) podobbně analyzuju úsek cca 2/4. Míchá se B a ~
(B)(~)~(~) zde je čisté ~ bez doznívajícího B.
(B)(~)(~)~ zde je čisté ~ na konci doznívající.
Modrá barva: segment testovaného vzorku.
Zvuky mají odlišný graf podle tóniny s jakou zvuk vyslovím.
Purpurový graf: Autokorelace.
Fialový graf: Frekvenční analýza.
Vše provedeno v Audacity.
Vzorek: Ba
Vzorek: B~
Detaily zde:
https://it-pomocnik.blogspot.com/2019/11/autokorelace-frekvencni-analyza.html
Vysvětlivky
~ reprezentuje zvuk následující zvuk B
B(a) znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na části písmene B, kde samohláska a nezasahuje do výběru.
(B)a znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na samohlásce "a".
(B)a(a) znamená, že analyzuju část, kde se prolíná "B" s "a", ale ne celý vzorek.
(B)~(~) podobbně analyzuju prostřední část (zvuk ~), kde se míchá B a ~.
(B)~(~)(~) podobbně analyzuju úsek cca 2/4. Míchá se B a ~
(B)(~)~(~) zde je čisté ~ bez doznívajícího B.
(B)(~)(~)~ zde je čisté ~ na konci doznívající.
Modrá barva: segment testovaného vzorku.
Zvuky mají odlišný graf podle tóniny s jakou zvuk vyslovím.
Purpurový graf: Autokorelace.
Fialový graf: Frekvenční analýza.
Vše provedeno v Audacity.
Vzorek: Ba
Vzorek: B~
Detaily zde:
https://it-pomocnik.blogspot.com/2019/11/autokorelace-frekvencni-analyza.html
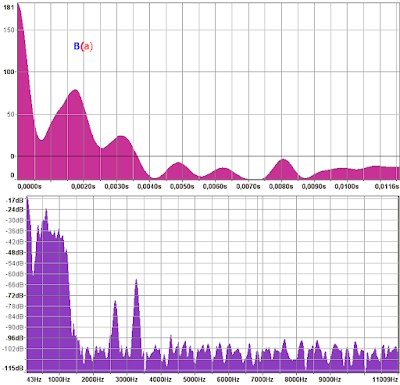
Autokorelace a frekvenční analýza
Příklady se slabikou Ba a B~
Vysvětlivky
~ reprezentuje zvuk následující zvuk B
B(a) znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na části písmene B, kde samohláska a nezasahuje do výběru.
(B)a znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na samohlásce "a".
(B)a(a) znamená, že analyzuju část, kde se prolíná "B" s "a", ale ne celý vzorek.
(B)~(~) podobbně analyzuju prostřední část (zvuk ~), kde se míchá B a ~.
(B)~(~)(~) podobbně analyzuju úsek cca 2/4. Míchá se B a ~
(B)(~)~(~) zde je čisté ~ bez doznívajícího B.
(B)(~)(~)~ zde je čisté ~ na konci doznívající.
Modrá barva: segment testovaného vzorku.
Zvuky mají odlišný graf podle tóniny s jakou zvuk vyslovím.
Purpurový graf: Autokorelace.
Fialový graf: Frekvenční analýza.
Vše provedeno v Audacity.
Vzorek: Ba
Vzorek: B~
Detaily zde:
https://it-pomocnik.blogspot.com/2019/11/autokorelace-frekvencni-analzyza-2.html
Vysvětlivky
~ reprezentuje zvuk následující zvuk B
B(a) znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na části písmene B, kde samohláska a nezasahuje do výběru.
(B)a znamená, že jsem analýzu provedl na samohlásce "a".
(B)a(a) znamená, že analyzuju část, kde se prolíná "B" s "a", ale ne celý vzorek.
(B)~(~) podobbně analyzuju prostřední část (zvuk ~), kde se míchá B a ~.
(B)~(~)(~) podobbně analyzuju úsek cca 2/4. Míchá se B a ~
(B)(~)~(~) zde je čisté ~ bez doznívajícího B.
(B)(~)(~)~ zde je čisté ~ na konci doznívající.
Modrá barva: segment testovaného vzorku.
Zvuky mají odlišný graf podle tóniny s jakou zvuk vyslovím.
Purpurový graf: Autokorelace.
Fialový graf: Frekvenční analýza.
Vše provedeno v Audacity.
Vzorek: Ba
Vzorek: B~
Detaily zde:
https://it-pomocnik.blogspot.com/2019/11/autokorelace-frekvencni-analzyza-2.html
pátek 18. října 2019
Archiving in PHP using Streams; jak zazipovat archiv pomocí streamu
Narazil jsem na tento skvělý článek a abych ho neztratil, rozhodl jsem se ho přilepit sem
https://www.sitepoint.com/performant-reading-big-files-php/
Jak vytvořit archiv - konzumuje mnoho operační paměti!
Jak efektivně snížit náročnost na paměť s použitím filtru
Nevýhoda: archiv nepůjde otevří pomocí Windowsovského nástroje pro práci s archivem zip.
https://www.sitepoint.com/performant-reading-big-files-php/
Jak vytvořit archiv - konzumuje mnoho operační paměti!
// from filters-1.php
$zip = new ZipArchive();
$filename = "filters-1.zip";
$zip->open($filename, ZipArchive::CREATE);
$zip->addFromString("shakespeare.txt", file_get_contents("shakespeare.txt"));
$zip->close();
require "memory.php";Jak efektivně snížit náročnost na paměť s použitím filtru
Nevýhoda: archiv nepůjde otevří pomocí Windowsovského nástroje pro práci s archivem zip.
// from filters-2.php
$handle1 = fopen(
"php://filter/zlib.deflate/resource=shakespeare.txt", "r"
);
$handle2 = fopen(
"filters-2.deflated", "w"
);
stream_copy_to_stream($handle1, $handle2);
fclose($handle1);
fclose($handle2);
require "memory.php";
file_get_contents(
"php://filter/zlib.inflate/resource=filters-2.deflated"
);středa 16. října 2019
neděle 13. října 2019
PHP: flock and fwrite is not save, you can lose data
This is the same case as file_get_contents and file_put_contents. With all these functions you can lose data if multiple script are running same time, trying to read and write, esspecially write, the same file.
You can find some mentions here:
I have made lots of tests using all possible methods:
1. file_get_contents/file_put_contents with LOCK_EX flag used in T2-T3
2. fopen, fflock, fread, fclose, fopen, flock, fwrite, fflush, fclose in T5-T6
3. the same as in point 2, but without flock, using mkdir lock instead (T8, T9)
Please see the results here:
PHP: Results comparison of file_ (get) put_contents & f (read / write / flush)
The discussion in located on Czech server:
Also please notice you have another articles regarding the atomicity on this blog, I have written them in English.
You can find some mentions here:
PHP flock() alternative
A locking file cache in PHPI have made lots of tests using all possible methods:
1. file_get_contents/file_put_contents with LOCK_EX flag used in T2-T3
2. fopen, fflock, fread, fclose, fopen, flock, fwrite, fflush, fclose in T5-T6
3. the same as in point 2, but without flock, using mkdir lock instead (T8, T9)
Please see the results here:
PHP: Results comparison of file_ (get) put_contents & f (read / write / flush)
The discussion in located on Czech server:
PHP: Výsledky srovnání funkcí file_(get)put_contents & f(read/write/flush)
So you can see clearly, that none of these methods is reliable, but - this is important - this is unders certain very rare circumstances. This test depends on how many circles you make and how many scripts you run. I run 4 scripts (made 1 script in real, but this runs after 4 requests were made from different browsers). So you may minimize the lock by descriting the number of the loops from 50 to 10 or 6 and you can do the same if you run only 3 scripts. Nobody will run such script in real, this was only to try simulate hard traffic. Of sure this is not the same as to run DOS attack using JS loop sending requests to server or some more realistic remote action.Also please notice you have another articles regarding the atomicity on this blog, I have written them in English.
sobota 12. října 2019
PHP: file_get_contents/file_put_contents you can lose data!
As I have written in this article:
And prooved buffering by this tests on remote server:
Do not use this functions when you modify the file you are working with. Either use fflock, fread, fflush, ffwrite work-around or you can lose your data when you use file_get_contents/file_put_contents.
The reason why there is no mention about it on internet is that most programmers of website use databases for purposes of data modifications (instead of files).
Another interesting article about atomicity is at Czech (also read slovak comments). There are some interesting solution. This is also about non-atomic file solutions. But there is also mention that the file can be opened between fopen and flock, which explains why in my stests T5-T7 there were these problems. Read the article at English or translate it. Mr. Vrana also has a cool solution of page caching.
Read this:
And prooved buffering by this tests on remote server:
Do not use this functions when you modify the file you are working with. Either use fflock, fread, fflush, ffwrite work-around or you can lose your data when you use file_get_contents/file_put_contents.
The reason why there is no mention about it on internet is that most programmers of website use databases for purposes of data modifications (instead of files).
Another interesting article about atomicity is at Czech (also read slovak comments). There are some interesting solution. This is also about non-atomic file solutions. But there is also mention that the file can be opened between fopen and flock, which explains why in my stests T5-T7 there were these problems. Read the article at English or translate it. Mr. Vrana also has a cool solution of page caching.
Read this:
There's the problem of calling fopen and then flock. Between these two operations (at least I think), another instance of the script can enter and open that file (for reading). If the original fopen was opened for writing, you probably lose the data in that file.Read Jakub Vrána:
Probability increases with the number of processes working on the same task, which I write in the article. This is unrelated to PHP's intelligence - the operating system determines which process is going to be the turn - at any time it can remember that it will give the opportunity to another process.
PHP: Warning: file_get_content and file_put_content may lose your data
Warning: file_get_content and file_put_content may lose your data
For some reason you will not find this important information in manual, but if you need to access a file, modify it and then save it, so these functions are not suitable. You may lose your data. You were warned.
More information please follow the topic here:
PHP: Results of comparation file_get_contents & file_put_contents vs flock, fread, fflush, fwrite.
This means, that the functions are not suitable for many things like, saving users information (sign-up) to a file. You may do this with a carefull fopen, fflock (with LOCK_EX), fread, fclose, fopen (with LOCK_EX), fwrite, fclose and check the size after write. You need to check the size before write and after write but you need to clear the cache first: clearstatcache(); Then use filesize to get the correct size. Also count with the need to restore the file with copy(), if you find out that the size is incorrect. You need to do this manually if you don't want to use database.
You can see my benchmark tests which proofs, that the functions file_get_contents and file_put_contents use buffering, which means you do not have the correct data after you change your file. The functions will take the old copy of data from buffer, not the current data from disk (they will even not write the change data to disk). So yes, these functions are super fast, but for some operations they are not usable.
For some reason you will not find this important information in manual, but if you need to access a file, modify it and then save it, so these functions are not suitable. You may lose your data. You were warned.
More information please follow the topic here:
PHP: Results of comparation file_get_contents & file_put_contents vs flock, fread, fflush, fwrite.
It is not a collision between these two functions, both atomic and reliable. The problem is if you read, modify, and save the file. These three actions are not in one transaction and therefore you may lose data when you overlap. If you need such a use case, use the database. (by Kit)
This means, that the functions are not suitable for many things like, saving users information (sign-up) to a file. You may do this with a carefull fopen, fflock (with LOCK_EX), fread, fclose, fopen (with LOCK_EX), fwrite, fclose and check the size after write. You need to check the size before write and after write but you need to clear the cache first: clearstatcache(); Then use filesize to get the correct size. Also count with the need to restore the file with copy(), if you find out that the size is incorrect. You need to do this manually if you don't want to use database.
You can see my benchmark tests which proofs, that the functions file_get_contents and file_put_contents use buffering, which means you do not have the correct data after you change your file. The functions will take the old copy of data from buffer, not the current data from disk (they will even not write the change data to disk). So yes, these functions are super fast, but for some operations they are not usable.
Is file_get_contents & file_put_contents reliable or can lead to loss of data? Benchmark results
I was wondering what happens if multiple scripts are sharing same
file. I uploaded the test on remote server, where they use HDD to store
data. There were 7 tests total, but the family of 6 are compatible.
I have 7 files of different size which I uploaded to server and the test. It is loop which reads and writes data from the files.
There is 50 microseconds delay in the loop. The loop repeats 50x.
I measure the time needed to perform every circle.
The differences in the tests (T):
Using file_get_contents/file_put_contents
T2 - SOURCE <> TARGET - reads data from original file, writes data do different (new) file
T3 - SOURCE = TARGET - 1. copies data from original file to target; 2. reads source data -> writes data; 3. the point 3 is repeated: i.e I read the data which I have written. This test uses same file to write data.
T4 - SOURCE = TARGET - I repeated the same test as in T3 getting shorted times.
Using fopen, flock, fread, flock, fclose, fopen, flock, fopen, fwrite, fflush, fclock, fclose ... This is complicated code, but here I have tested the fflush. I also use clearstatcache, stat and touch and clearstatcache, filesize. To check validity. The tests T5 - T7 were less reliable than T2-T4 because sometimes the write operation failed. I tested the file size and when it was not correct, I copied (restored) the file back from original file.
T5: (fflush) SOURCE = TARGET
T6: (fflush) SOURCE <> TARGET
T7: (fflush) SOURCE <> TARGET + I have removed the 50 microseconds delay from the loop (It seems like the validity/reliability is worse when there is a delay).
I made 4 requests from 4 different browsers - so every test have 4 sets of data (7*50*4 values total).
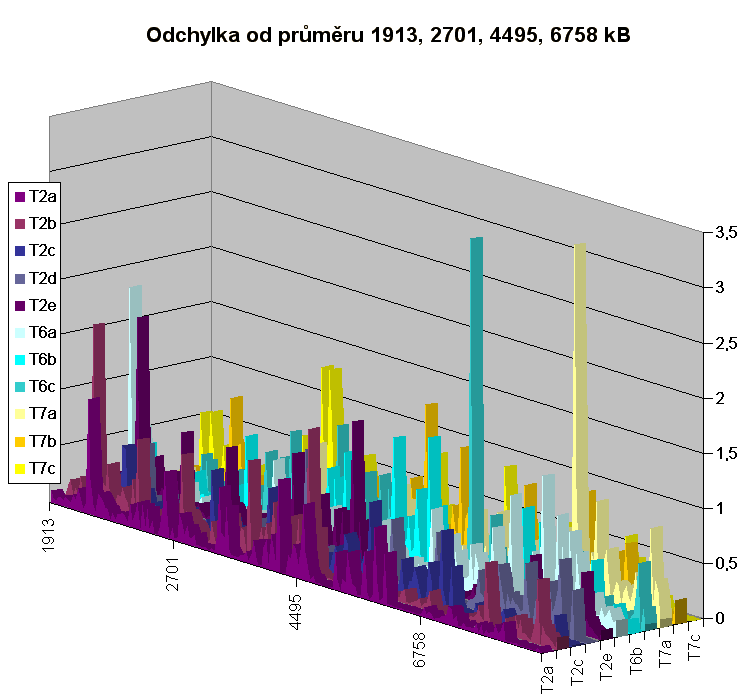
Now I have collected all data, created tables and diagrams. This is one diagram of many, showing minimal and maximal values of avarage value.
T4 yellow color and T3 green provides very small times so they are suspicious. For example T4 avarage times are these: 0,001
T5-T7 just show normal times as expected - the bigger the file the bigger the time needed to proccess. Fairly slow as expected from HDD and 4 scripts running at the same time.
So my question here is:
Does the results of T3-T4 mean, that the file_read_contents and file_put_contents are not reliable for this type of job? To me it looks like they simply do not read the data from file but they are copied from buffer, which means, that old data are saved, not the current data been changed by concurent script. I would welcome more information. I spent a lot of time searching for answers but did not found clear answer. I did this tests because I need proofs. You man want to use my scripts but I am not sure if can I paste here the 6 scripts?
Now I will add just the fflush test number 7 which is most useful.
"; usleep(5000); } endfor; $s = fread($fp, $fsize ); $success = flock($fp, LOCK_UN); if ( $success === false ) die("; r flock release failed; "); $success = fclose($fp); if ( $success === false ) die("; fclose failed; "); // 10 - data loaded , $p - browser if ( $success ) { $result = touch("$sname",strlen($s),$p); if ( $_DEBUG_ ) echo "; TOUCH: $result;"; } else die("fclose FAIL."); if ( strlen($s)<60 ) echo "*$s LENGTH:".strlen($s)."
"; } clearstatcache(); $st = stat("$tname"); if ( $_DEBUG_ ) echo "; 2) prevAccess by ".$st['mtime']." fsize is ".$fsize."; "; // WRITE OPERATION WITH LOC_EX $fp = fopen($tname, "w"); $locked = false; $locked = flock($fp, LOCK_EX); if ( $locked ) { // acquire an exclusive lock $success = fwrite($fp, $s); if ( $success === false) echo "; w FAILED;"; else if ( $_DEBUG_ ) echo " $success B written; "; $success = fflush($fp);// flush output before releasing the lock if ( $success === false ) echo "; flush FAILED; "; $success = flock($fp, LOCK_UN); // release the lock if ( $success === false ) echo "; release FAILED; "; $success = fclose($fp); if ( $success === false ) echo "; fclose FAILED; "; clearstatcache(); // needed for filesize and touch $fsize = filesize($tname); if ($original_size>$fsize) { echo "; WRITE FAILED, restoring;"; $original_fname = "$n"; $result = copy($original_fname, $tname); if ($result == false ) die(" TOTAL FAILTURE: copy failed."); else echo " RESTORED;"; } else { if ($fsize === 0) echo "! THE FILE WAS NOT WRITTEN: data length: ".strlen($s)." fsize: $fsize RESOURCE: $fp
"; if ( $success ) touch("$tname",$fsize,$p); } } else { echo "Couldn't get the lock!"; } $time_elapsed_secs = microtime(true) - $start; if ( $time_elapsed_secs === 0 ) echo " FAILED "; echo "time: $time_elapsed_secs s
"; } } switch ( $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT'] ): // FF 1: case "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv:49.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/49.0": $p = 1; break; // Chrome: case "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/49.0.2623.112 Safari/537.36": $p = 2; break; // OPERA: case "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/49.0.2623.112 Safari/537.36 OPR/36.0.2130.80": $p = 3; break; endswitch; copy("523","523.txt"); copy("948","948.txt"); copy("1371","1371.txt"); copy("1913","1913.txt"); copy("2701","2701.txt"); copy("4495","4495.txt"); copy("6758","6758.txt"); test("523",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("948",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("1371",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("1913",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("2701",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("4495",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("6758",$p,$_DEBUG_); die; echo "php: " . phpversion(); ?> PHP echo "php: " . phpinfo(); ?>
Note: This is not a request for test, this is just request for review.
Also: Please do not be confused by the yellow color curve. There are two yellow colors. The T4 yellow is almost no visible on the diagram because it has very low values.
If you want to solve this question, follow the topic here.
<50 1="" and="" by="" clearstatcache="" echo="" filesize="" for="" fsize="filesize($sname);" i="" if="" mtime="" needed="" original_size="" prevaccess="" size="" sname="" st="" start="microtime(true);" touch=""><60 br="" echo="" length:="" s="" strlen="">
I have 7 files of different size which I uploaded to server and the test. It is loop which reads and writes data from the files.
There is 50 microseconds delay in the loop. The loop repeats 50x.
I measure the time needed to perform every circle.
The differences in the tests (T):
Using file_get_contents/file_put_contents
T2 - SOURCE <> TARGET - reads data from original file, writes data do different (new) file
T3 - SOURCE = TARGET - 1. copies data from original file to target; 2. reads source data -> writes data; 3. the point 3 is repeated: i.e I read the data which I have written. This test uses same file to write data.
T4 - SOURCE = TARGET - I repeated the same test as in T3 getting shorted times.
Using fopen, flock, fread, flock, fclose, fopen, flock, fopen, fwrite, fflush, fclock, fclose ... This is complicated code, but here I have tested the fflush. I also use clearstatcache, stat and touch and clearstatcache, filesize. To check validity. The tests T5 - T7 were less reliable than T2-T4 because sometimes the write operation failed. I tested the file size and when it was not correct, I copied (restored) the file back from original file.
T5: (fflush) SOURCE = TARGET
T6: (fflush) SOURCE <> TARGET
T7: (fflush) SOURCE <> TARGET + I have removed the 50 microseconds delay from the loop (It seems like the validity/reliability is worse when there is a delay).
I made 4 requests from 4 different browsers - so every test have 4 sets of data (7*50*4 values total).
Now I have collected all data, created tables and diagrams. This is one diagram of many, showing minimal and maximal values of avarage value.
T4 yellow color and T3 green provides very small times so they are suspicious. For example T4 avarage times are these: 0,001
0.001 0.002 0.003 0.002 0.004 0.003 0.004 0.001 0.004 0.001 0.004 0.001 0.004 0.002 0.003 0.001 0.001 0.003 0.003 0.006 0.007 0.002 0.003 0.004 0.004 0.019 0.019 T5-T7 just show normal times as expected - the bigger the file the bigger the time needed to proccess. Fairly slow as expected from HDD and 4 scripts running at the same time.
So my question here is:
Does the results of T3-T4 mean, that the file_read_contents and file_put_contents are not reliable for this type of job? To me it looks like they simply do not read the data from file but they are copied from buffer, which means, that old data are saved, not the current data been changed by concurent script. I would welcome more information. I spent a lot of time searching for answers but did not found clear answer. I did this tests because I need proofs. You man want to use my scripts but I am not sure if can I paste here the 6 scripts?
Now I will add just the fflush test number 7 which is most useful.
PHP
clearstatcache();
$_DEBUG_ = false;
echo "Lock and flush tester.".time()."
";
die;
while ( time()<1570787996 )
{
usleep(500);
}
function test($n, $p, $_DEBUG_){
$sname = "$n"; // source
$tname = "$n.txt";// target
echo "
$n at "
.time().""; usleep(5000); } endfor; $s = fread($fp, $fsize ); $success = flock($fp, LOCK_UN); if ( $success === false ) die("; r flock release failed; "); $success = fclose($fp); if ( $success === false ) die("; fclose failed; "); // 10 - data loaded , $p - browser if ( $success ) { $result = touch("$sname",strlen($s),$p); if ( $_DEBUG_ ) echo "; TOUCH: $result;"; } else die("fclose FAIL."); if ( strlen($s)<60 ) echo "*$s LENGTH:".strlen($s)."
"; } clearstatcache(); $st = stat("$tname"); if ( $_DEBUG_ ) echo "; 2) prevAccess by ".$st['mtime']." fsize is ".$fsize."; "; // WRITE OPERATION WITH LOC_EX $fp = fopen($tname, "w"); $locked = false; $locked = flock($fp, LOCK_EX); if ( $locked ) { // acquire an exclusive lock $success = fwrite($fp, $s); if ( $success === false) echo "; w FAILED;"; else if ( $_DEBUG_ ) echo " $success B written; "; $success = fflush($fp);// flush output before releasing the lock if ( $success === false ) echo "; flush FAILED; "; $success = flock($fp, LOCK_UN); // release the lock if ( $success === false ) echo "; release FAILED; "; $success = fclose($fp); if ( $success === false ) echo "; fclose FAILED; "; clearstatcache(); // needed for filesize and touch $fsize = filesize($tname); if ($original_size>$fsize) { echo "; WRITE FAILED, restoring;"; $original_fname = "$n"; $result = copy($original_fname, $tname); if ($result == false ) die(" TOTAL FAILTURE: copy failed."); else echo " RESTORED;"; } else { if ($fsize === 0) echo "! THE FILE WAS NOT WRITTEN: data length: ".strlen($s)." fsize: $fsize RESOURCE: $fp
"; if ( $success ) touch("$tname",$fsize,$p); } } else { echo "Couldn't get the lock!"; } $time_elapsed_secs = microtime(true) - $start; if ( $time_elapsed_secs === 0 ) echo " FAILED "; echo "time: $time_elapsed_secs s
"; } } switch ( $_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT'] ): // FF 1: case "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1; rv:49.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/49.0": $p = 1; break; // Chrome: case "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/49.0.2623.112 Safari/537.36": $p = 2; break; // OPERA: case "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/49.0.2623.112 Safari/537.36 OPR/36.0.2130.80": $p = 3; break; endswitch; copy("523","523.txt"); copy("948","948.txt"); copy("1371","1371.txt"); copy("1913","1913.txt"); copy("2701","2701.txt"); copy("4495","4495.txt"); copy("6758","6758.txt"); test("523",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("948",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("1371",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("1913",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("2701",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("4495",$p,$_DEBUG_); test("6758",$p,$_DEBUG_); die; echo "php: " . phpversion(); ?> PHP echo "php: " . phpinfo(); ?>
Notice: 523 means the filesize is 523 kB.
Note: This is not a request for test, this is just request for review.
Also: Please do not be confused by the yellow color curve. There are two yellow colors. The T4 yellow is almost no visible on the diagram because it has very low values.
If you want to solve this question, follow the topic here.
<50 1="" and="" by="" clearstatcache="" echo="" filesize="" for="" fsize="filesize($sname);" i="" if="" mtime="" needed="" original_size="" prevaccess="" size="" sname="" st="" start="microtime(true);" touch=""><60 br="" echo="" length:="" s="" strlen="">
Přihlásit se k odběru:
Komentáře (Atom)
Jede jede vláček kolejáček (TS) noty
Auth:ST 1c, 2c(-2), 3a, 4a(-2), 1G, 2G, 3c, 4H (úvodní markery #FF0000 jako c treble, pak a treble, G open) 1a, 2a, 3G, 4G, 1G(-2...
Štítky
.profile
adm
administrace
Adobe
Aho-Corasick
AI
akcelerace
alfa transparence
analýza
AND
any
aplikace
apt
ar
archiv
asociativní pole
atomicity
audacity
audio
audio redirect
autentifikace
automatizace
awk
balíčkovací systém
bash
beacon
beacon_hint
benchmark
Bézierovy křivky
bezpečnost
biblehub
BJT
blogger
boolean
Braessův paradox
brainstorming
BRE
buffer
buffering
bufferované čtení
Cache-Conrol
Cloudflare
code
Collector Cut-off
ColorManager
colorpicker
common
compare
config
cookies
CPU
CPU pipe
crop
css
CSS3
curl
current code
cut
čas
data loss
data lost
data transfer reliability
datasheet
datetime.strptime
deb
deb-systemd-helper
debian
debián
depricated
development
dict
dioda
diody
disonance
doprava
dpkg
dpkg -S
dpkg-deb
drivers
EBO
editace
efekt
Emitter Cut-off Current
eps
ETag
evtest
exclude
exec
Expires
extrakce jediného
extrakce názvu balíčku souboru
extrakce obrázků
extrakce souboru .deb
fflock
fflush
ffmpeg
FIFO
file read
file write
file_get_contents
file_get_contents/file_put_contents
file_put_contents
filter
find
first_install.sh
flock
Fly-back dioda
font-face
fonty
fóra
formant-preserving morphing
fotorezistor
fread
functions
funkce
FuzzyWuzzy
fwrite
gate
gate drive
GDVfs
gedit
gedit-common
geolokace
getdata
Ghostscript
GIO
glib
gnome
gnome settings
GNU Privacy Guard
gnupg
gpg
gradient-background
grafika
grep
grep -v
groupadd
grub
grub update
gs
gsettings
gtk
gtk.css
gtk+
hebrejština
history
hlavičky
HS
html
html 5
https
hudba
hunspell
charakterizace
chatGPT
chroot
chyba
ICES
IGBT
Image
img sizes
img srcset
impedance
implementace
imshow
inference
inkscape
inrush current
install
IQ
jalový výkon
javascript
javescript
jednocení seznamů
js
jsonData
kapacita součástek
klávesnice
koeficient zesílení
komponenty xFce
komunikace se serverem
koncept
konfigurace
kontejner
korekce barev
Krita
KSF
kvantifikátor
kytara
Last-Modified
lazy caching
led
LEFT JOIN
librosa
ligatury
light-locker
lightdm
linux
list
log
m3u
maják
manuál
map
mapování
maskování
maskování hlasu
maskování služby
masky
matplotlib
Max-Age
measure
melodie
memory
měření
meta
MFCC
MFCC koeficienty
mint
Mint 21.3
Mint xFce
míry
mlt
modules
moralizace
morphologie
MOSFET
mount
moviepy
multimedia
mysql
náběhový proud
napěťová ochrana
nastavení šablony
návod
návrh
nel
Network Error Logging
NLP
normalizace šedi po resize
not
Notifications
noty
NTFS
nth-child
oblasti
oblékání
ochrana
okruhy přátel
OpenVINO IR formát
oprava
oprava balíčku
optočlen
org.gnome.desktop.screensaver
org.gnome.nm-applet
ořezové masky
OSHB
otázky
otázky_jazyky
otázky_moralismu_řešení
overlay
ovladače
panely
parsování
path
pdf
personifikace
photorec
php
php 4
php 5
php 6
php 7
php 8
phpbb
phpBB3
PipeWire
pitch
plus
PN přechody
pnp
pole
Policykit
postscript
práva
profilování
program
prune
průraz
přeinstalování
překlad
přepěťová ochrana
přepolování
příkazy
připojení k síti
připojení k wifi
pseudokódd
pstoedit
pulse
PulseAudio
PWM regulátory
pydub
python
python3
pytorch
ramdisk
RBE
RDSon
read
reaktance
rectifier
regex
regulace vstupního napětí
reinstall
relyability
remount
replace
restore
reverzní geolokace
RIGHT JOIN
rm
robotický hlas
role
rozvržení disků pro OS linux a data databází
řešení
samba
scan
scroll
sdílení
sdílení souborů
Sec-Fetch-Dest
Sec-Fetch-Mode
Sec-Fetch-Site
Sec-Fetch-User
Secure Shell
sed
Set Cookie
show-manual-login
show-remote-login
shunt
schemas
schémata
schottka
signal morphing
sink
skript
skupiny
sledovanost
sloupce
slučování seznamů
služby
small
song
sort
soubory
soundfile
spínané zdroje
spínání
splines
split
spojování
správa diskových zařízení
SQL
ssh
stabilizace napětí
stahování
stíny
stream
stream redirect
string
strojové učení
stropové učení
subprocess.call
supplicant
svg
syntax
systemctl
systemd-logind
T5
tabulka
tabulky
Tangentové úsečky
tar
témata
tepelná ztráta
terminologie
test
text-shadow
themes
thermal runaway
time
timestamp
tkinter
tr
transformace
transistor
transition
transpose
tranzistor
tranzistory
TS
ttf
tuple
tvorba otázek
TVS
typografie
ubuntu
účiník
udiskd
udisks
unconfined
underrun
unity-greeter
update
usermod
uživatelé
va charakteristika
vala
věda
vektorová grafika
Vgs
video
virtual devices
vocoder
Vth
vyhledávání
vyhledávání soborů
výkon
vynechání adresářů
vytvoření playlistu
vývoj
webovka
while
wpa
wpa_supplicant
wrapovací funkce
x
xandr
xapp-watt
xargs -I
xed
xed-common
xfdesktop
xml
xmp
XOR
Xorg
Xorg Thumbnails
xrandr
závislosti
zdánlivý výkon
zdroj
zenerka
zenerovo napětí
zip
zip archiv
zkratky
zpomalení
zpracování textu
zrychlení
zvuk
Žalmy
-
PRETEXT Důvod proč chci z md5sums extrahovat jen informace o .xml je, že další soubory jako dokumentace .gz a obrázky .png apod. by bylo ho...
-
Adresář includes pokračování functions_content.php (includes) gen_sort_selects(&$limit_days, &$sort_by_text, &$sort_days, ...